Inference of 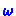 -Languages from Prefixes
-Languages from Prefixes
Authors: Colin de la Higuera and Jean-Christophe Janodet
Source: Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence Vol. 2225, 2001, 364 - 377.
Abstract.
Büchi automata are used to recognize languages of infinite words.
Such languages have been introduced to describe the behavior of
real time systems or infinite games. The question of inferring
them from infinite examples has already been studied, but it may
seem more reasonable to believe that the data from which we want
to learn is a set of finite words, namely the prefixes of accepted
or rejected infinite words. We describe the problems of
identification in the limit and polynomial identification in the
limit from given data associated to different interpretations of
these prefixes: a positive prefix is universal (respectively
existential) when all the infinite words of which it is a prefix
are in the language (respectively when at least one is); the same
applies to the negative prefixes. We prove that the classes of
regular ![]() -languages (those recognized by Büchi automata) and of
deterministic
-languages (those recognized by Büchi automata) and of
deterministic ![]() -languages (those recognized by deterministic Büchi
automata) are not identifiable in the limit, whichever
interpretation for the prefixes is taken. We give a polynomial
algorithm that identifies the class of safe languages from
positive existential prefixes and negative universal prefixes. We
show that this class is maximal for polynomial identification in
the limit from given data, in the sense that no superclass can
even be identified in the limit.
-languages (those recognized by deterministic Büchi
automata) are not identifiable in the limit, whichever
interpretation for the prefixes is taken. We give a polynomial
algorithm that identifies the class of safe languages from
positive existential prefixes and negative universal prefixes. We
show that this class is maximal for polynomial identification in
the limit from given data, in the sense that no superclass can
even be identified in the limit.
©Copyright 2001 Springer